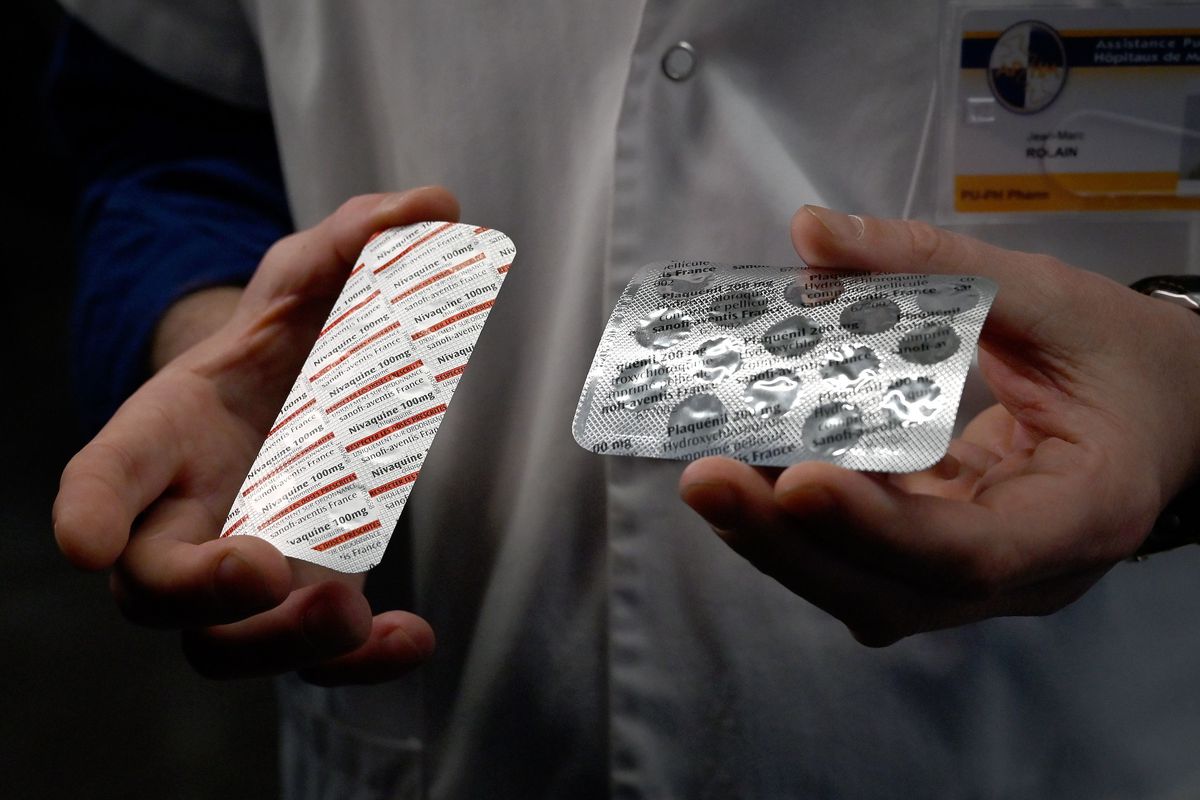
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has recently given a warning to the public regarding the use of the anti-malarial drug, Hydroxychloroquine, for the treatment of COVID-19 symptoms at home.
Currently, there is no scientific evidence to support the effectiveness of the drug for managing the coronavirus infection. However, there has been a lot of hype about medicine, especially amongst social media users.
Many have called Hydroxychloroquine a ‘miracle drug’ and have supported its use in people who have been tested positive for COVID-19.
The situation has also posed difficulties for frontline health care workers since many patients have started requesting the use of the medication due to misinformation about its effectiveness.
In addition, there is also an increased risk for people relying on self-medication and taking anti-malarial drugs for curing the coronavirus infection at home for the purpose of prevention.
Till now, only a few small-scale trials have shown the potential benefits of Hydroxychloroquine for the treatment of COVID-19. However, as suggested by health authorities, the drug cannot be used until there are confirmed results from bigger, well-designed trials.
Therefore, medicines such as Chloroquine or Hydroxychloroquine should only be used when they are prescribed by a licensed health practitioner. Such medicines should not be taken without consultation as they can lead to serious adverse effects on health.
An official warning was issued by the FDA on April twenty-fourth when there were reported cases of people who had developed a number of issues as a result of taking Hydroxychloroquine.
In the COVID-19 patients who had been given Hydroxychloroquine either alone or in combination with other drugs, the researchers had noted serious negative effects such as faster than normal heartbeats and abnormal health rhythms.
Additionally, some patients with the coronavirus infection who had received the drug had also died as a result.
Regardless of initial trials showing the effectiveness of Hydroxychloroquine in patients who had tested positive for coronavirus infection, more and more recent studies are reporting its negative impact on the patients.
Among the first studies, one was conducted with a small number of participants in France. The study used a combination of Hydroxychloroquine and the broad-spectrum antibiotic azithromycin.
The findings of the study were circulated soon after its positive result on different social media platforms even though the researchers themselves reported limitations and flaws in the design.
The President of the United States, Donald Trump, had also reportedly tweeted about the trial and promoted the use of the drug, thereby further adding to its hype, which led to him receiving major backlash from the medical community.
RELATED: Health Experts Warn Against Trump’s Dangerous Advice
Even the journal in which the French study’s findings were published issued a statement regarding the major flaws in the design of the study soon after the buildup of the hype.
Now, other clinical trials and research on anti-malarial drugs for COVID-19 are showing negative effects of the drugs which heavily outweigh its potential positive impact shown by earlier studies.
In fact, one of the trials conducted on testing the drug Chloroquine was stopped soon after the researchers noted the development of fatal heart conditions in the patients who were given high doses of the drug.
Another research reported the chances of dying in the patients with the coronavirus infection who were given azithromycin and Hydroxychloroquine were as high as in patients who take either of the drugs.
More precisely, the drugs did not make any difference in people with COVID-19. On the other hand, the chances of survival were seen to be higher in people who received the current standard treatment for coronavirus infection.
This shows that there is no scientific evidence yet to support the use of Hydroxychloroquine or any drugs for the treatment of COVID-19. Instead, they may worsen the infection and cause life-threatening conditions.